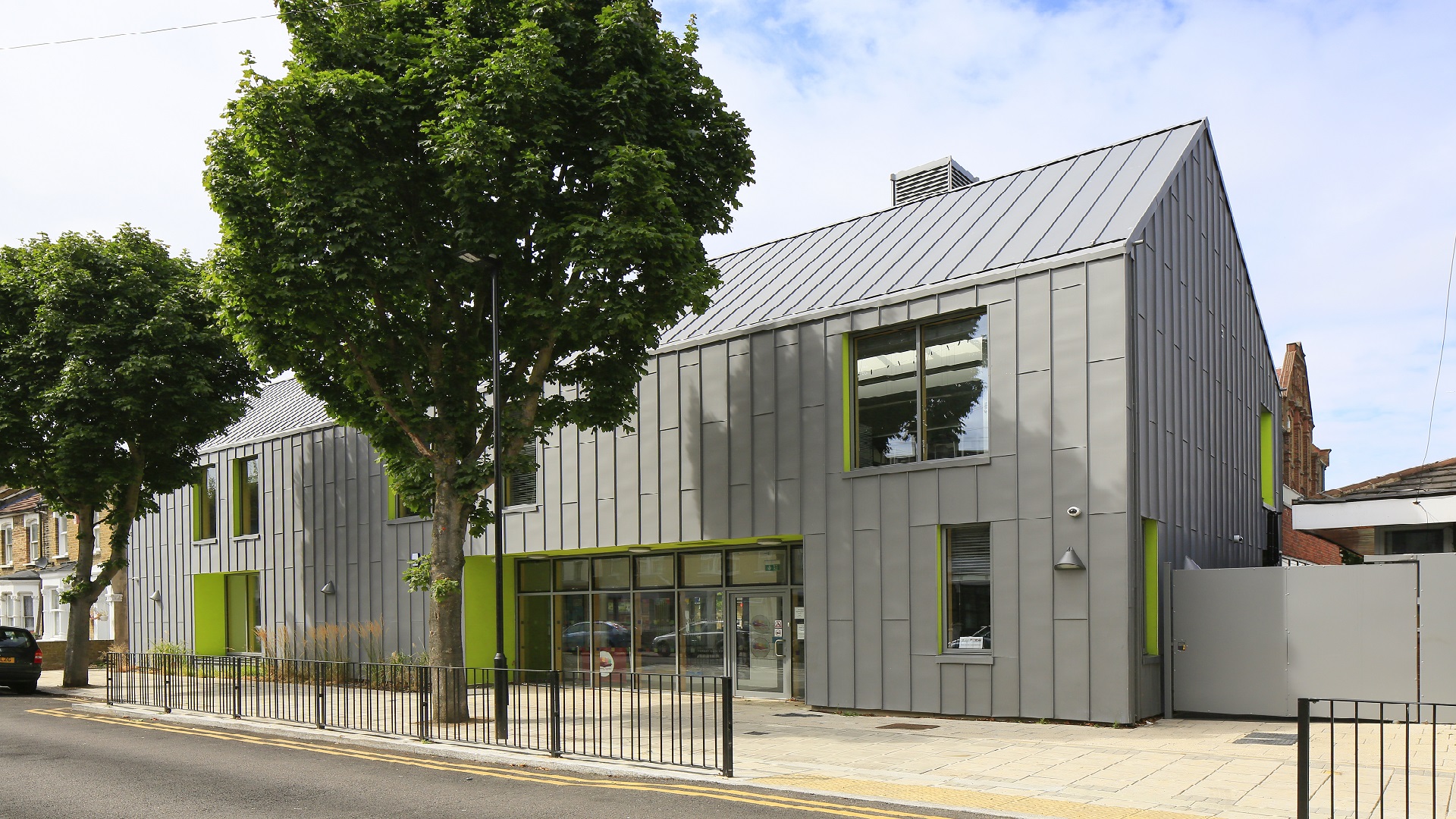
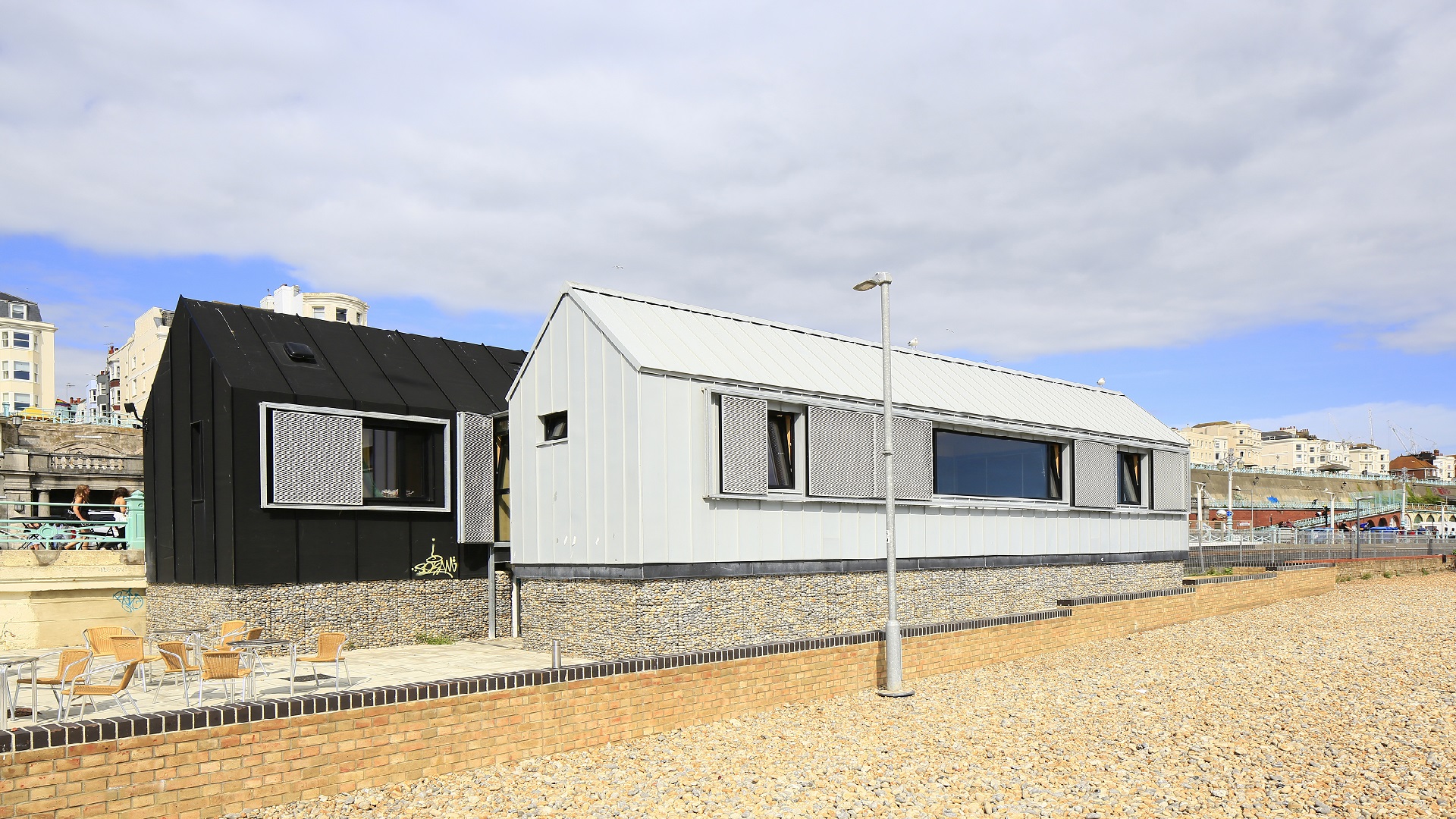
Roof & Wall Build-Ups
VMZINC must not only be installed according to our recommendations but also designed to them as well.
Basic requirements
VMZINC can be installed on non-vented warm roof build-ups as well as on vented cold roof build-ups. For standing seam build-ups a roof would have a slope of no more than 70º; above this slope it should be considered wall cladding. All wall cladding should be ventilated. VMZINC will only give a warranty for recommended build-ups and details. The minimum slope for zinc roofs is 1:12 (4.76⁰ or 8.3%) as built.
Definition of warm roof in the North America
Warm non-ventilated and cold ventilated roofs are two terms which do not always denote the same ideas to all building professionals. In order to put the warm non-ventilated roof system into context, we will refer to it as a roof where there is absolutely no vented space within the roof build-up and furthermore the entire roof structure is on the warm side of the insulation. Whilst there are a few very limited exceptions in North America this means that the roof structure is generally below the insulation.
Fundamental Elements of the System
- VMZINC PLUS must be used on all warm roof build-ups
- Delta VMZINC Membrane must be used
- The substrate must be continuous and even and the correct fixing clips must be used
- A fully supported continuous vapor barrier must be installed (bitumen-backed aluminum foil). Polythene films are not acceptable
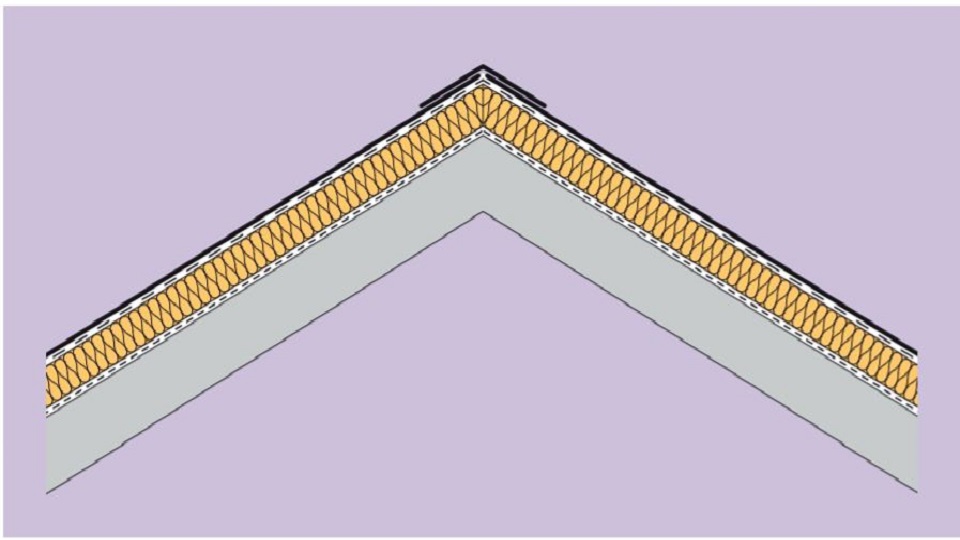
Warm Roof: Continuous layer of insulation covering a fully supported vapour barrier.
Fundamental elements of the system:
- VMZINC PLUS must be used on all warm roof build-ups.
- VMZINC Membrane must be used (breather membrane).
- The substrate must be continuous and even and the correct fixing clips must be used.
- A fully supported continuous vapour barrier, Aludex Max, must be installed (bitumen-backed aluminium foil). Polythene films are not acceptable.
- For humidity class 5 (swimming pools) the Compact roof with Foamglas must be used. This build-up, as with the Structural roof, carries a BBA certificate.
Definition of cold roof in the North America
Cold ventilated roofs and warm non-ventilated roofs are two terms which do not always denote the same ideas to all building professionals. In order to put the cold ventilated roof system into context, we will refer to it as a roof where there is a continuous air space of at least 2” between the substrate supporting the zinc and the insulation. This air space must be a vented space with openings generally at the eaves and the ridge. Linear air vents must be at least ⅜” wide and are commonly protected by insect mesh. It is always good practice to include a vapor control layer in the build up and this should be installed on the warm side of the insulation.
Elements of the System
- VMZINC PLUS must be used for all Standing Seam roofing applications.
- Delta VMZINC Membrane must be used for all substrates with the exception of vented open gap skip sheathing.
- The substrate must be continuous and even, and the correct fixing clips must be used.
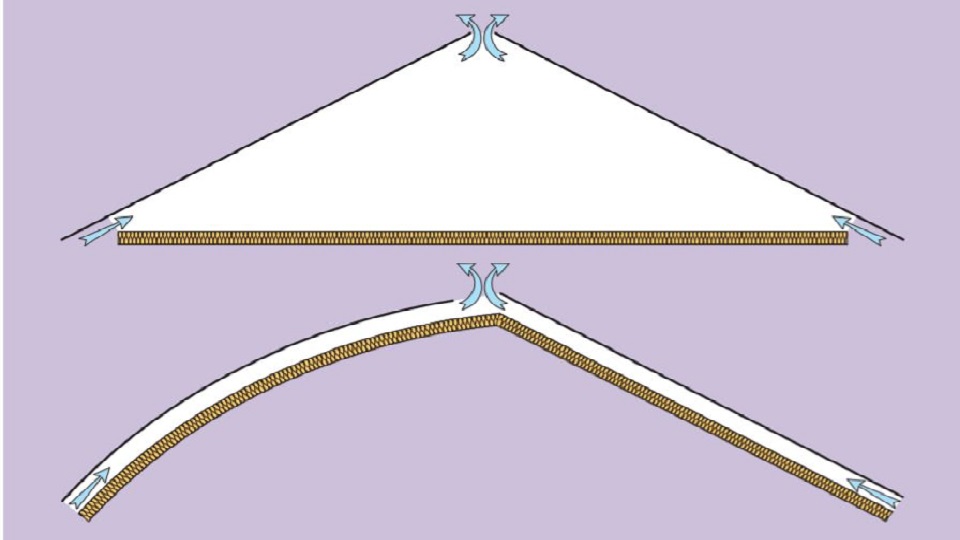
Cold Roof: Air inlets and outlets are generally linear (at least 10mm open) but can be individual. The ventilation must correspond to BS: S250: 2002.
Fixing clips
All standing seam panels must have a fixed area of at least 5 one-piece fixing clips which do not allow any thermal expansion or contraction. It should be noted that when items such as PV panels or snow retention systems are being fitted directly to the zinc roof a calculation of shear load must be carried out.
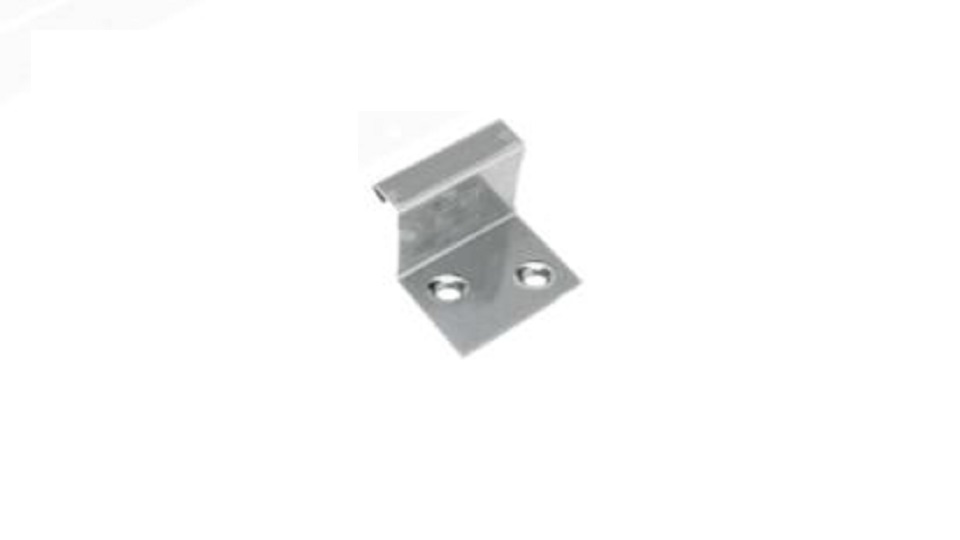

Fixed Clip
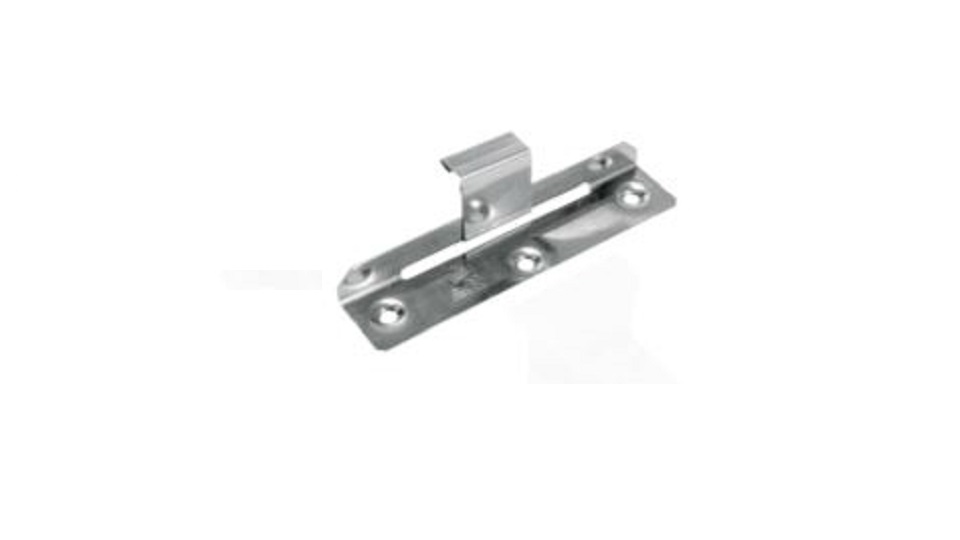

Sliding Clip
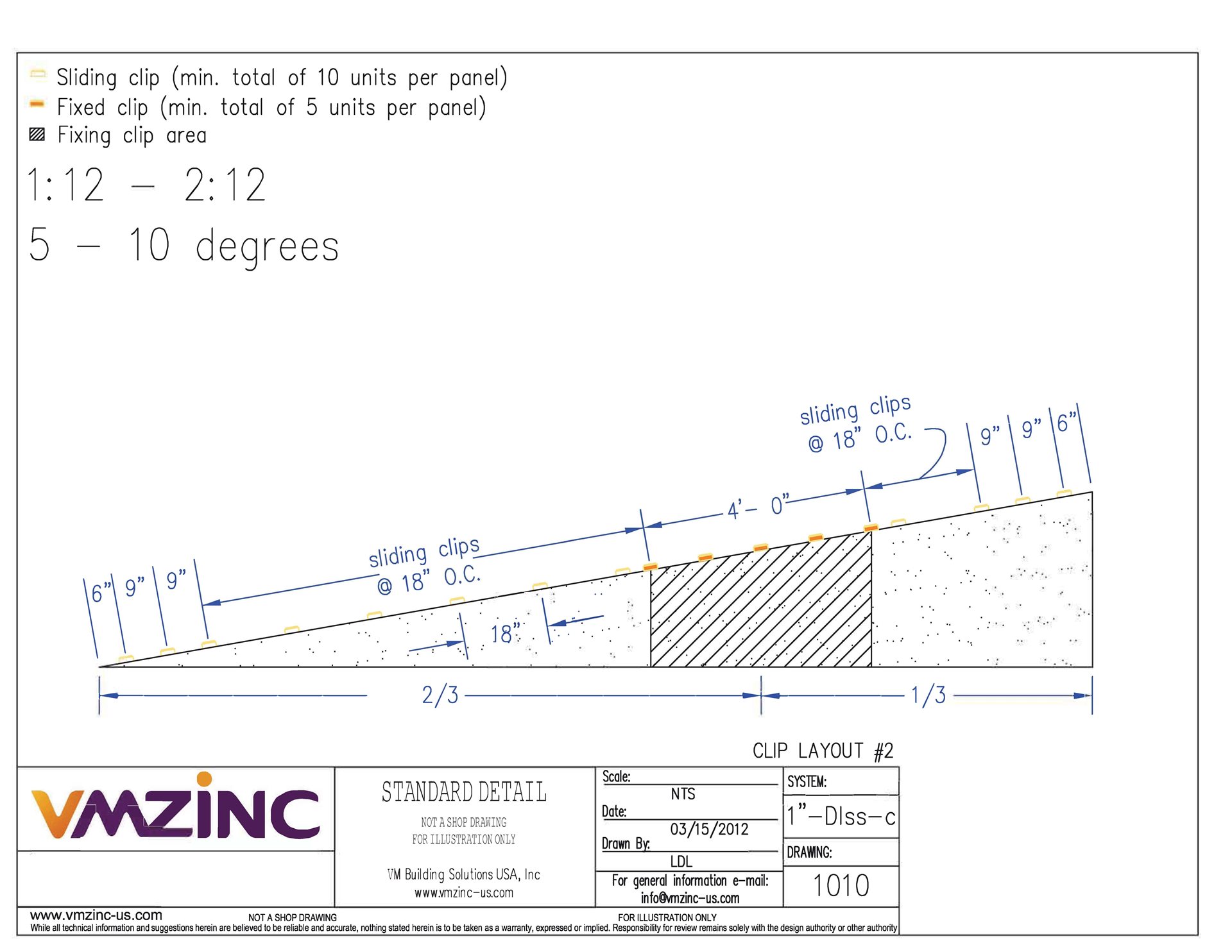
This will determine whether by increasing the number of fixed clips will be sufficient or not to deal with the possible shear loads. Maximum clip spacing is 18” with this reducing to 9” along the edges of the roof (at least 48” or 1/8 of the projected roof) and 6” where two edges meet.
Panel size
Standing seam roof panels can be manufactured as 16 7/8” (428mm) or 15 7/8” (403mm) standard widths depending on seam height, 1” (25mm) or 1.5” (38mm) , narrower panels should be used in exposed locations. The maximum standard length for roofing panels is 13m. Roof panels are generally 0.7mm thick, however, for long panels or exposed sites 0.8mm thick zinc can be considered. Please consult us concerning panel sizes for façade systems.
Noise
As zinc is a relatively soft metal, impact noise is rarely an issue. However, if the building owner does have concerns the use of a warm roof build-up would reduce not only impact noise but also possible noise created by pressure differences in a vented air space which is a prerequisite of a vented roof.
Façade Systems
A wide range of VMZINC façade systems exists. The majority follow the rainscreen principle where the panels are fixed to rails on a vertical wall incorporating a 1.5” (38mm) vented space. Standing seam and flat lock panels are fixed to a continuous support and can be considered as wall cladding for slopes above 70º. As all the systems are vented it may be necessary to include fire breaks which can involve compartmentalising the façade using flashings or compatible intumescent fire stops.
VMZINC and VMZINC PLUS
Zinc is a metal that has been used to clad the exterior of buildings for many years and as such is resistant to water. However, this is only the case in the presence of carbon dioxide (which is present in air). If zinc is installed on a substrate that limits the amount of air that can be in contact with its back surface it is possible that this will induce the formation of white rust. It is for this reason that VMZINC (no backside coating) can only be used on roofing when vented open gap softwood boarding is used as a substrate. VMZINC is also acceptable on vented rainscreen facades. For all other roof build-ups VMZINC PLUS must be used.
VMZINC PLUS consists of VMZINC (in all finishes) having a 60μm coating applied to the underside thus allowing a more varied amount of substrates to be used and eliminating the risk of the formation of white rust on the underside of the zinc standing seam panels. VMZINC PLUS resists to an abrasion of 40 litres when tested in accordance with ASTM D 968.
Continuous professional development presentation (CPD)
VMZINC offer a, RIBA accredited, CPD Seminar to architects and contractors.
Life Cycle
A Life Cycle Analysis (LCA) is a standardised tool used to assess the environmental characteristics of building products.

