Facades – underlying principals
Introduction
VMZINC has been used as a material to clad facades for many decades. Initially traditional roofing systems such as standing seam panels were installed as `roofs on walls`. Flat lock panels have also been installed for many decades. Both of these systems require vented continuous substrates and are commonly installed by traditional hard metal roofing contractors. Over the past two decades rainscreen facades have become very popular and VMZINC offers a number of these rainscreen systems.
Joint types
VMZINC wall panels can be joined using three mechanical joints:
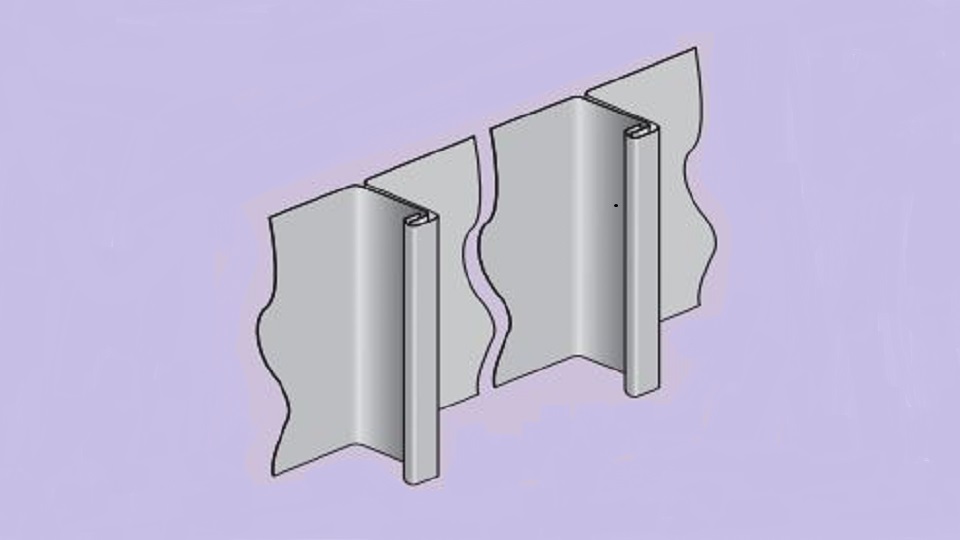
Standing Seam
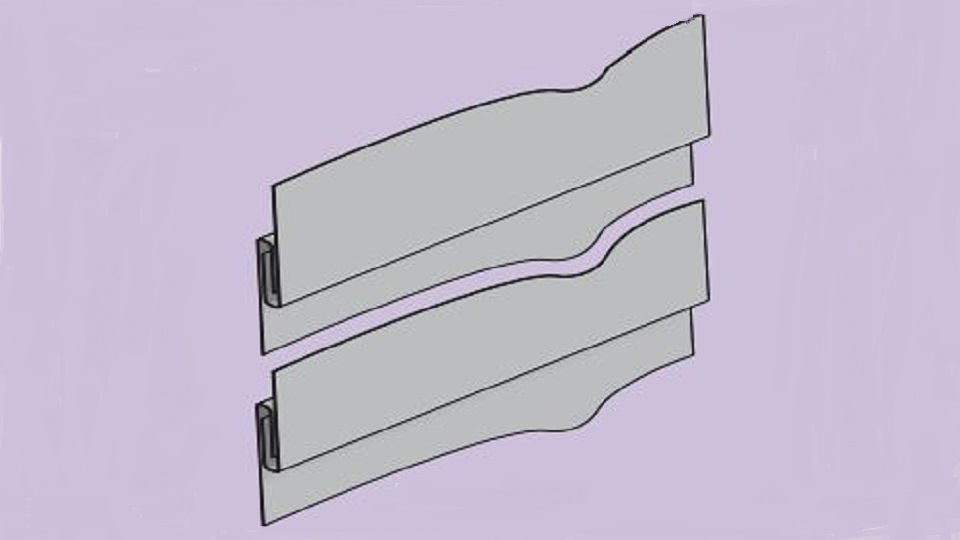
Flat Lock
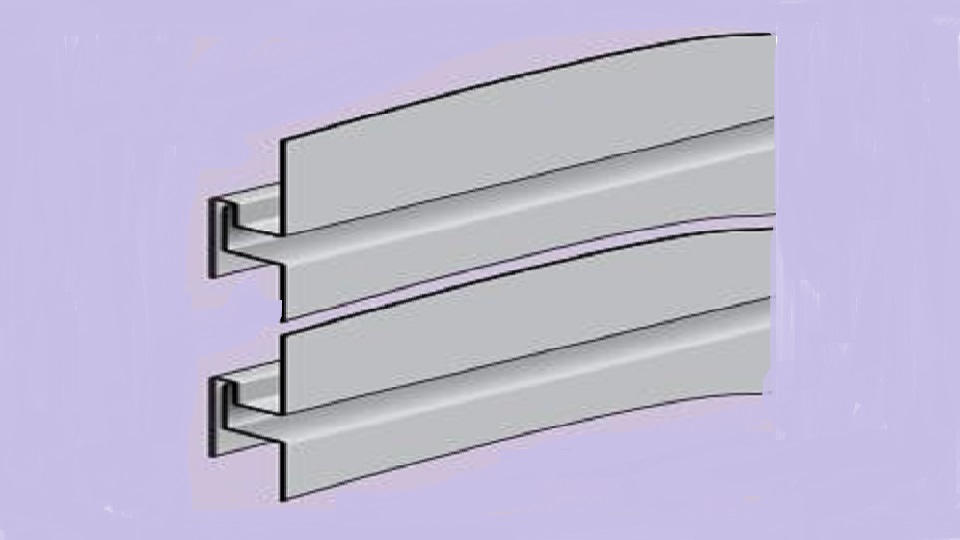
Reveal
Non-Combustible Facades (type A and B Construction)
For buildings where combustible materials such as plywood cannot be used, galvanised steel decks can be used as a substrate for the flat lock and standing seam panels. VMZINC Material is non-combustible and has been tested to AS 1530.1 - Combustibility for Building Materials. The metal deck must be at least 0.48mm thick and have dimensions allowing clips to be attached at the required spacings. For all surfaces such as sills, parapets, etc the substrate must be continuous. The vented cavity can be fire stopped using continuous vertical cavity barriers and intumescent horizontal cavity barriers.
Traditional fully supported zinc clad facades
Initially traditional roofing systems such as standing seam panels were installed as `roofs on walls`. Flat lock panels have also been installed for many decades. Both of these systems require vented continuous substrates and are commonly installed by traditional hard metal roofing contractors.
Rainscreen zinc facades
A raincreen facade is an outer skin that is back-ventilated by an air space that is 38mm deep. The system can be used on both new build and renovation but always allows the outer layer to breathe whilst the inner layer deals with thermal insulation and air leakage. All joints are dry and do not use any form of sealant.